What is Heat Pipe Thermal Conductivity
If you’ve ever wondered what heat pipe thermal conductivity is and why it matters in cooling technology, you’re in the right place. Heat pipe thermal conductivity refers to the ability of heat pipes to efficiently transfer heat from one point to another, making them a vital component in many electronic cooling systems. In this article, we’ll explain what heat pipe thermal conductivity is, how it works, and why it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal device performance.
What Is Thermal Conductivity?
In simple terms:
- A low k value means the material blocks heat (like wood or air).
How Does It Work?
- Materials like metals have high thermal conductivity — heat travels through them easily. That’s why metals feel cold or hot quickly.
- Materials like wood or plastic have low thermal conductivity — they don’t let heat pass through easily, so they act as insulators.
Understanding thermal conductivity helps engineers and designers make better choices about materials to manage heat, whether it’s cooling electronics, building energy-efficient homes, or designing cooking tools.
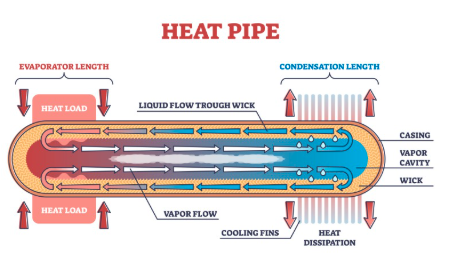
What Is Heat Pipe Thermal Conductivity?
This cycle makes heat pipes extremely efficient, transferring heat thousands of times better than metal alone.
Factors Affecting Heat Pipe Thermal Conductivity
Several things influence how efficiently a heat pipe moves heat. Understanding these helps engineers design better cooling systems.
- Length of the Heat Pipe
Longer heat pipes usually transfer heat better because there’s more space for the vapor inside to travel. But if they get too long, it can slow down heat transfer.
- Diameter (Width) of the Heat Pipe
Wider heat pipes carry more liquid and move more heat, but if too wide, liquid flow back can slow down, reducing efficiency.
- Amount of Heat (Heat Load)
If the heat gets too high, the pipe can dry out, reducing its effectiveness.
- Temperature Difference
A bigger temperature difference between the hot and cool ends makes heat move faster, but too large a gap can damage the pipe.
- Working Fluid
The liquid inside the pipe matters a lot. Good fluids evaporate easily (high latent heat) and flow smoothly (low viscosity). Common choices include water, ammonia, or refrigerants.
- Wick Structure and Material
Materials with good capillary action, like sintered metals or grooved surfaces, help keep the liquid moving efficiently.
- Operating Temperature Range
If the pipe is too hot or too cold, the fluid won’t evaporate or condense properly, making heat transfer less efficient.
- Orientation and Angle
The way a heat pipe is positioned affects how gravity helps the liquid inside flow. If the pipe is tilted or upside down, it can slow the liquid from flowing back, making the heat pipe less efficient.
- Surface Quality and Contact
How well a heat pipe touches the parts it’s cooling is important. Rough or uneven surfaces can block heat flow, making cooling less effective. Nanofluids
Adding tiny particles called nanoparticles (like copper oxide) to the fluid inside a heat pipe can improve heat transfer. These particles help the fluid conduct heat better, making the cooling more efficient.
- Critical Heat Flux
This is the maximum heat the pipe can carry before the wick stops working well, causing the liquid to dry out. Going beyond this limit damages performance and the pipe itself.
- Manufacturing Quality
Manufacturing quality directly affects a heat pipe’s performance. High-quality production ensures the wick is properly made, surfaces are smooth, and the working fluid flows evenly. This results in more efficient and reliable heat transfer.
Choosing the right size, liquid, temperature, and quality helps heat pipes transfer heat effectively, keeping devices cool and running smoothly.
Importance of Heat Pipe Thermal Conductivity in Cooling Technology
- Super Efficient at Moving Heat
Heat pipes can transfer heat way better than solid metals like copper, sometimes 4 to 100 times better! This means they quickly move heat away from hot parts, helping keep electronics cool and working well.
- Prevents Overheating
As electronics get smaller and more powerful, they create more heat in cramped spaces. Heat pipes help by moving that heat away from hot spots to cooler areas, keeping devices safe from overheating.
- Small and Lightweight Cooling
Heat pipes are very effective at transferring heat, which allows cooling systems to be smaller and lighter. This makes them ideal for devices where saving space and reducing weight are important, such as smartphones, laptops, and wearable gadgets.
- Quiet and Dependable
Heat pipes move heat without needing fans or electricity, so they work silently and reliably. This makes them ideal for quiet environments like hospitals or home electronics.
- Useful Everywhere
Heat pipes aren’t just for electronics, they’re also used in planes, cars, and industrial machines because they handle heat efficiently in many different environments.
The excellent heat-moving ability of heat pipes is key to making compact, reliable, and effective cooling solutions. This helps devices last longer and perform better in many industries.




